Before we jump into the technique of spread spectrum clocking, let us understand why it it been used so widely. All the electronic devices emits Electro-magnetic radiation. This electro magnetic radiation can interfere with the surrounding systems like other on-board systems, radio, TV etc. Because of this governments across the world have been regulating the amount of EMI (Electro Magnetic Interference) an electronic system can emit. EMI can interrupt, degrade or reduce the performance of the system. These can cause simple degradation of the data to the total loss of the data.
Electro magnetic radiation in digital systems can in many cases exceed the regulatory guidance because of the periodic nature of the signals. Clocks in the digital systems are periodic. It means they have a fixed frequency. Because of the fixed frequency, the radiated power has peak values. This due to the harmonics. Continuous repeated radiations builds up harmonics that amplifies the radiated power which can cause severe noise interference to the surrounding systems. Hence the solution we can think of is to avoid the periodicity (fixed frequency). You might wonder how can we implement this. Nowadays SSC (Spread Spectrum Clocking) has become widely used method to reduce the peak EMI power.
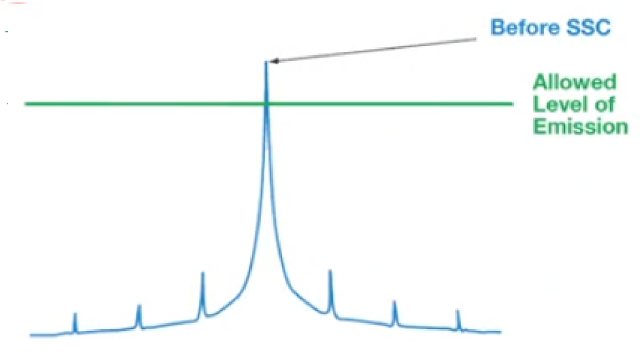
In the picture above the radiated power concentrates in one particular frequency. Hence we can see that the emitted power has peak value which very well exceeds the allowed levels of emission. In order to avoid this peak emission powers, spread spectrum clocking allows us to distribute the clock frequency over a range of frequencies there by we could avoid harmonics and therefore peak power emissions.
There are 4 important parameters in the SSC, they are :
- Modulation index : amount of frequency (or spread) as a relative percentage of the input or the carrier frequency.
Example : 1% spread means an input/carrier frequency of 100MHz is spreading from 99MHz to 101MHz.
- Modulation frequency : the rate at which the input or carrier frequency will change between the min and max range.
Example : with 1% spread on input frequency of 100MHz, modulation frequency says the rate in which the frequency changes between 99 to 101MHz.
How can we implement SSC ?
- Modulation profile : how the clock frequency is modulated between min and max frequency range.
- Spread type : there are two types of spreads down spread or the center spread.
- down spread : the spread range is bellow the input frequency. from 98MHz to 100MHz for -2% down spread for above example.
- center spread : the spread range distributes evenly with center as input frequency. 99MHz to 101MHz for 1% center spread.
How can we implement SSC ?

I think the admin of this web page is genuinely working hard in favor of his website, because here
ReplyDeleteevery data is quality based stuff.
my web site: Clocking systems Johannesburg